Religious Communities in India
Relevant for sociology optional Paper- 2 (Unit- 12 : Social Structure)
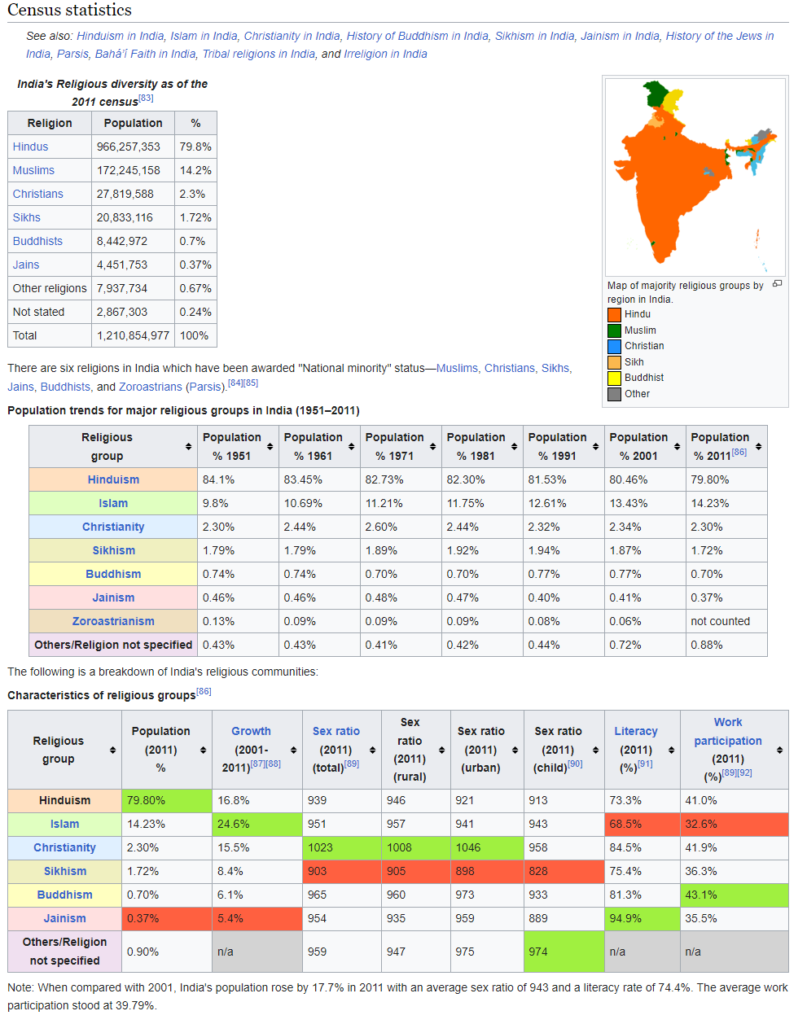
India is known for its cultural diversity, which is evident in the coexistence of various religious communities in the country. Religion has played a significant role in shaping the identity of Indian society, and its impact is visible in all aspects of life, including culture, politics, and social relations. According to the 2011 Census of India, Hindus form the majority of the population, followed by Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, and others.
Hinduism, which is the oldest religion in India, is believed to have originated in the Indus Valley Civilization around 5000 years ago. It is a complex and diverse religion, with numerous gods and goddesses, rituals, and traditions. Hinduism is also characterized by a hierarchical caste system, which has been a subject of controversy and criticism over the years. Despite its flaws, Hinduism has been a unifying force for the Indian people, and it continues to influence the country’s culture and way of life.
Islam, which was introduced to India in the 7th century, is the second-largest religion in the country. The spread of Islam in India was mainly through trade and conquest, and it was particularly prominent in the northern part of the country. The Mughal Empire, which ruled India from the 16th to the 19th century, was an Islamic state that left a significant impact on Indian culture and architecture. Today, Muslims form a significant minority in India and are concentrated in the northern and eastern states.
Christianity in India has a long and rich history, dating back to the arrival of St. Thomas, one of the apostles of Jesus Christ, in the 1st century AD. The arrival of European colonizers in the 16th century led to the spread of Christianity in India, particularly in the southern and northeastern regions. Today, Christians form a small but significant minority in India and are spread throughout the country.
Sikhism, which was founded by Guru Nanak in the 16th century, originated in the Punjab region of India. It is a monotheistic religion that emphasizes the importance of community service, equality, and the pursuit of knowledge. Sikhs have played an important role in Indian history, particularly during the Mughal era when they fought for their rights and freedoms. Today, Sikhs form a significant minority in India and are concentrated in the Punjab region.
Buddhism, which originated in India in the 6th century BC, is based on the teachings of Gautama Buddha. It is a non-theistic religion that emphasizes the importance of meditation, mindfulness, and compassion. Although Buddhism declined in India after the 12th century, it continues to be an important religion in other parts of the world, particularly in Southeast Asia.
Jainism, which was founded in the 6th century BC, is a religion that emphasizes the importance of non-violence, self-control, and spiritual purification. Jains are known for their strict adherence to vegetarianism and their reverence for all forms of life. Although Jains form a small minority in India, their influence on Indian culture and philosophy has been significant.
Apart from these major religions, India is also home to numerous other religious communities, such as the Baha’i Faith, Zoroastrianism, and Judaism. Each of these communities has a unique history and tradition that has contributed to the cultural diversity of India.
Despite the coexistence of multiple religious communities in India, religious tensions and conflicts have been a persistent problem in the country. The partition of India in 1947, which resulted in the creation of Pakistan, was a traumatic event that led to widespread violence and the displacement of millions of people. The Babri Masjid demolition in 1992, the Godhra train burning in 2002, and the Delhi riots in 2020 are some of the recent examples of religious conflicts in India. These conflicts often stem from political or economic motives, and they have a devastating impact on the lives of ordinary people.
To address these issues, the Indian government has implemented various policies and initiatives to promote religious harmony and tolerance. The Constitution of India guarantees freedom of religion and prohibits discrimination on the basis of religion. The government has also set up various institutions, such as the National Commission for Minorities, to protect the rights of religious minorities and to address their grievances.
Apart from the government, civil society organizations and religious leaders have also played an important role in promoting interfaith dialogue and cooperation. The annual Urs festival in Ajmer, which attracts thousands of people from different religious backgrounds, is a testament to the power of religious harmony and unity.
In conclusion, religious communities in India are diverse and complex, with each community contributing to the cultural and social fabric of the country. While religious tensions and conflicts continue to be a problem, efforts are being made to promote religious harmony and tolerance. As India continues to grow and develop, it is essential to ensure that the country’s rich religious diversity is celebrated and that all communities are treated with respect and dignity.
For more such free UPSC notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel. https://t.me/triumphias
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC – Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php


