Features of Caste System
Relevant for sociology optional Paper- 2 (Unit- 12 : Social Structure)
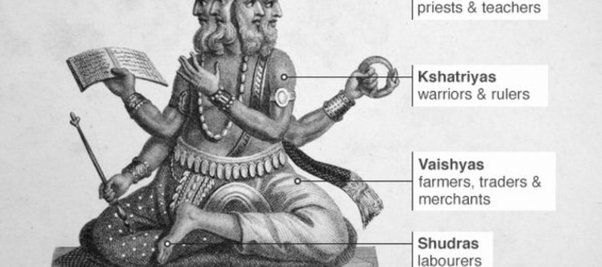
The caste system is a social structure that has existed in India for centuries. It is a hierarchical system where individuals are classified based on their birth, occupation, and social status. The caste system is a complex structure with various features that define it. In this essay, we will explore the features of the caste system and examine their impact on Indian society.
One of the key features of the caste system is that it is a hereditary system. Caste is determined by birth and is passed down from generation to generation. This means that a person’s caste is determined at birth and cannot be changed during their lifetime. This system is deeply ingrained in Indian society and has been a part of the cultural and religious fabric of the country for centuries.
Another feature of the caste system is its hierarchical nature. The system is divided into four main castes – Brahmins, Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras – with each caste occupying a specific place in the social hierarchy. Brahmins are at the top of the caste system and are considered to be the highest caste. They are followed by Kshatriyas, Vaishyas, and Shudras, in that order. The Shudras are at the bottom of the caste system and are considered to be the lowest caste.
The caste system also has sub-castes or jatis, which are based on occupation and social status. Each sub-caste has its own set of rules and regulations, and members of different sub-castes are not allowed to intermarry or socialize with each other. This has led to the formation of thousands of sub-castes, each with its own unique identity and culture.
One of the most controversial features of the caste system is the practice of untouchability. This practice is rooted in the belief that some castes are impure and polluting, and that contact with them can contaminate members of higher castes. Those who belong to the lowest castes, such as the Shudras and the Dalits, are considered to be untouchable and are forced to perform menial and degrading tasks such as cleaning, garbage collection, and manual scavenging.
Another feature of the caste system is the strict rules regarding marriage and social interaction. Members of different castes are not allowed to marry or socialize with each other, and breaking these rules can result in social ostracism and even violence. This has led to the perpetuation of caste-based discrimination and has limited the social and economic mobility of individuals from lower castes.
The caste system also has a significant impact on economic opportunities and access to resources. Members of higher castes are more likely to have access to education, employment, and other resources, while those from lower castes are often marginalized and excluded from these opportunities. This has led to significant disparities in wealth and income, with members of higher castes controlling a disproportionate amount of resources and power.
The caste system also has a significant impact on politics and governance in India. Political parties often use caste-based identity politics to mobilize voters and win elections. This has led to the formation of caste-based vote banks and has perpetuated caste-based discrimination and inequality.
Despite the numerous negative features of the caste system, it has also played a significant role in shaping Indian society and culture. Caste-based identities have influenced art, music, literature, and other cultural expressions in India, and have contributed to the diversity and richness of Indian culture. The caste system has also provided a sense of identity and belonging to members of different castes, and has helped to maintain social order and stability in Indian society.
In conclusion, the caste system is a complex social structure with numerous features that define it. It is a hereditary, hierarchical system with strict rules regarding social interaction and marriage. The practice of untouchability and the significant disparities in economic opportunities and access to resources are among the most negative features of the caste system. Despite its many flaws, the caste system has played a significant role in shaping Indian society and culture, and its legacy continues to influence Indian society today. Efforts to reform and eliminate the caste system have been ongoing, but progress has been slow and challenging. Ultimately, the caste system represents a significant challenge to India’s quest for social justice, equality, and progress, and its elimination will require significant societal, political, and cultural change.
For more such free UPSC notes, Articles, News & Views Join our Telegram Channel. https://t.me/triumphias
Click the link below to see the details about the UPSC – Civils courses offered by Triumph IAS. https://triumphias.com/pages-all-courses.php


